You’ve just been tasked with upgrading the network for a multi-story office building.
Now, you’re facing the challenge of picking the right cable jacketing material.
What type of jacketing meets fire safety regulations? How durable does it need to be in a high-traffic area? Will it affect the overall network performance?
In this post, we’ll go over the key considerations to help you make the best choice for both safety and efficiency.

(fabrikasimf/Freepik)
Why Cable Jacketing Matters
The cable jacket acts as the first line of defense for any cable.
It shields the inner conductors from physical damage and environmental factors like moisture, heat, and chemicals.
In high-traffic areas or places where cables face stress, the jacket keeps everything secure and in good working order.
Cable jacketing also helps prevent issues like abrasion or cuts that may lead to malfunctions or even safety risks.
Which Cable Jacket Material Is Best for Your Installation
The ideal material for cable jacketing depends on where and how you plan to use the cables.
Each type offers different benefits, so understanding their strengths helps you make the right call.
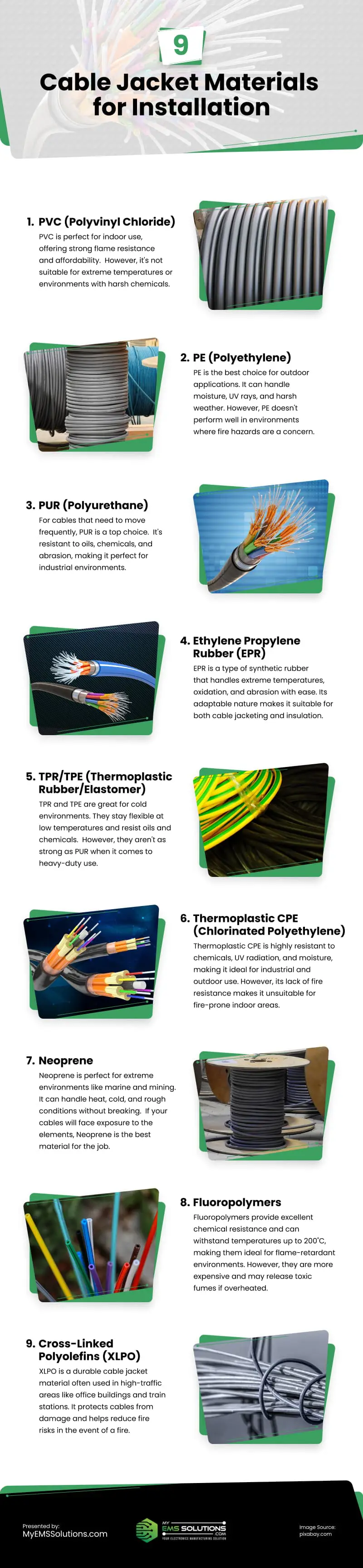
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is perfect for indoor use, offering strong flame resistance and affordability.
It works well in residential and office settings where physical stress is low.
However, it’s not suitable for extreme temperatures or environments with harsh chemicals.
PE (Polyethylene)
PE is the best choice for outdoor applications. It can handle moisture, UV rays, and harsh weather.
You’ll find it in direct burial applications that face long-term exposure to harsh weather.
However, PE doesn’t perform well in environments where fire hazards are a concern.
PUR (Polyurethane)
For cables that need to move frequently, PUR is a top choice.
It’s resistant to oils, chemicals, and abrasion, making it perfect for industrial environments.
If flexibility and durability are your top priorities, PUR will meet your needs.
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR)
EPR is a type of synthetic rubber that handles extreme temperatures, oxidation, and abrasion with ease.
Its adaptable nature makes it suitable for both cable jacketing and insulation.
That’s why you’ll find installers using it in power cables for outdoor environments and industrial machinery where durability and resilience are essential.
TPR/TPE (Thermoplastic Rubber/Elastomer)
TPR and TPE are great for cold environments. They stay flexible at low temperatures and resist oils and chemicals.
However, they aren’t as strong as PUR when it comes to heavy-duty use.
TPR and TPE work best for light industrial settings where cables need to bend without breaking.
Thermoplastic CPE (Chlorinated Polyethylene)
Thermoplastic CPE is excellent in chemically harsh environments.
Its resistance to chemicals, UV radiation, and moisture makes it a top pick for industrial and outdoor use.
But since CPE lacks fire resistance, it’s not the best option for indoor fire-prone areas.
Neoprene
Neoprene is perfect for extreme environments like marine and mining.
It can handle heat, cold, and rough conditions without breaking.
If your cables will face exposure to the elements, Neoprene is the best material for the job.
Fluoropolymers
Fluoropolymers offer superior chemical resistance compared to most other cable jacket materials.
Withstanding temperatures up to 200˚C, these cables are ideal for environments requiring flame-retardant properties.
However, they come with a higher price tag and can release toxic fumes upon overheating.
Cross-Linked Polyolefins (XLPO)
XLPO is a specialized cable jacket material that keeps wires safe and durable.
Builders often choose it for places where lots of people gather, like office buildings or train stations.
XLPO protects cables from damage while also reducing risks if a fire ever breaks out.
Selecting The Right Material
To choose the best material for your cable jacketing needs, consider the following table highlighting the strengths and limitations of each option:
| Material | Best For | Watch Out For |
|---|---|---|
| PVC | Home and office use | Extreme temperatures |
| PE | Outdoor installations | Fire-prone areas |
| PUR | Factory floors | Higher cost |
| EPR | Industrial machinery | May not suit all applications |
| TPR/TPE | Cold environments | Heavy-duty use |
| CPE | Chemical plants | Indoor fire risks |
| Neoprene | Harsh outdoor conditions | Higher cost, less flexibility |
| Fluoropolymers | Flame-retardant needs | Releases toxic fumes upon overheating |
| XLPO | Transportation systems | Higher cost |
This overview can serve as a starting point for your selection process.
However, always consider your specific environmental and operational requirements when making a final decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Cable Jacket Selection Impact My PCB Assembly Process?
Your cable jacket choice affects how you handle and connect cables during PCB assembly. Flexible jackets like PUR make routing easier in tight spaces. Tougher jackets might require special tools or techniques for stripping and termination.
Can I Use the Same Cable Jackets for Through-Hole and SMT Assembly?
You can use the same jacket materials for both assembly types. However, consider heat resistance for SMT processes. Some jackets withstand higher temperatures better, which matters during reflow soldering.
How Do Cable Jackets Factor Into EMS Box Build Projects?
Cable jackets play a crucial role in EMS box builds. You’ll need to choose jackets that match your enclosure’s environment. Consider factors like internal heat, external exposure, and flexibility for maintenance access when selecting jacket materials.
What Should I Consider for Cable Jackets in Medical Device Manufacturing?
For medical devices, prioritize jackets that meet ISO 13485 standards. Look for materials that resist sterilization chemicals and don’t off-gas. Also, consider jackets that support frequent cleaning and disinfection routines.
How Do RoHS Regulations Affect My Choice of Cable Jackets for Electronic Manufacturing?
RoHS compliance limits your use of certain materials in cable jackets. You’ll need to avoid jackets containing restricted substances like lead or certain flame retardants. Many modern jacket materials already meet RoHS standards, but always double-check with your supplier.
Final Verdict
Understanding the different cable jacket materials is key to successful installations. While this guide provides a solid foundation, remember that technology and materials constantly evolve.
Always consult with experts or cable assembly services for the most up-to-date information. Your specific project may have unique requirements, so don’t hesitate to seek professional advice.
With the right knowledge and support, you’ll ensure your cabling solution meets both current needs and future challenges.
Video
Infographic
The cable jacket is the first line of defense for any cable. The ideal material depends on how and where the cables will be used. Understanding the strengths of each type helps you make the best choice. Check out the infographic for more information.